The Impact Of Cloud Computing On Businesses
Cloud computing has profoundly impacted businesses by offering scalable resources, significant cost savings, and enhanced flexibility that foster innovation and improved collaboration. This shift allows companies of all sizes to access advanced technologies and focus on strategic goals rather than infrastructure management.
Key benefits for businesses
Cost efficiency and resource optimization:

Cloud computing eliminates the need for large, upfront capital expenditures on hardware and data centers. The “pay-as-you-go” model turns capital expenses into operational ones, allowing businesses to optimize budgets and only pay for the resources they use.
Scalability and flexibility:
Businesses can easily and quickly scale their IT resources up or down to meet fluctuating workloads, such as seasonal traffic spikes, without investing in permanent infrastructure. This agility enables companies to respond rapidly to market changes and pursue growth opportunities.
Enhanced collaboration and mobility:

Cloud-based tools like Google Workspace and Microsoft 365 enable real-time collaboration among geographically dispersed teams, which is essential for remote and hybrid work models. Employees can access data and applications from any device with an internet connection, boosting productivity and mobility.
Innovation and competitive advantage:
Cloud platforms provide ready access to advanced technologies like AI, machine learning, and big data analytics that were once only available to large enterprises. This accelerates product development and time-to-market, giving businesses a competitive edge and fostering a culture of experimentation.
Improved data security and business continuity:
Reputable cloud providers invest heavily in robust security measures like data encryption, access controls, and threat monitoring, often surpassing what individual businesses can achieve on their own. Cloud-based backup and disaster recovery solutions ensure business continuity and minimize data loss in the event of hardware failures or cyberattacks.
Challenges to consider
While the benefits are substantial, businesses must navigate certain challenges to maximize their cloud investment
Data security and privacy concerns:

Storing sensitive information on third-party servers requires a thorough understanding of the provider’s security protocols and compliance with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA.
Vendor lock-in:
Migrating from one cloud provider to another can be complex and costly due to proprietary technologies and service differences. A multi-cloud or hybrid strategy can help mitigate this risk and ensure flexibility.
Downtime and connectivity issues:
Reliance on a stable internet connection means potential service disruptions or latency if the connection is poor. It is crucial to have contingency plans in place to handle outages.
Cost management complexity:
Although cloud computing is often cost-efficient, businesses may face unexpected or hidden costs related to data transfer fees, storage, and over-provisioning if resources are not continuously monitored and optimized.
Skill gaps and integration challenges:
Implementing and managing cloud solutions may require new skills within the workforce. Integrating cloud services with existing legacy systems can also be a daunting and complex task.
Cloud computing has fundamentally reshaped business operations by enabling digital transformation, optimizing costs, accelerating innovation, and enhancing collaboration across various industries. By moving away from on-premises infrastructure, companies gain immense flexibility and access to advanced technologies that foster growth and a competitive edge.
benefits of Cloud Computing On Businesses
Cost efficiency and operational agility
Reduced capital expenditures (CapEx):
Businesses eliminate the need for large, upfront investments in physical servers, data centers, and networking hardware. Cloud costs shift to an operational expenditure (OpEx) model, freeing up capital for strategic initiatives.
Pay-as-you-go model:
This pricing structure allows companies to pay only for the resources they consume, avoiding the waste associated with over-provisioning for peak loads. Costs can easily be scaled down during slow periods for budget optimization.
Higher operational efficiency:
Managed cloud services reduce the burden on internal IT teams, as maintenance, updates, and infrastructure management are handled by the cloud provider. This allows IT staff to focus on more strategic work that adds business value.
Scalability, flexibility, and innovation
Elastic resource scaling:
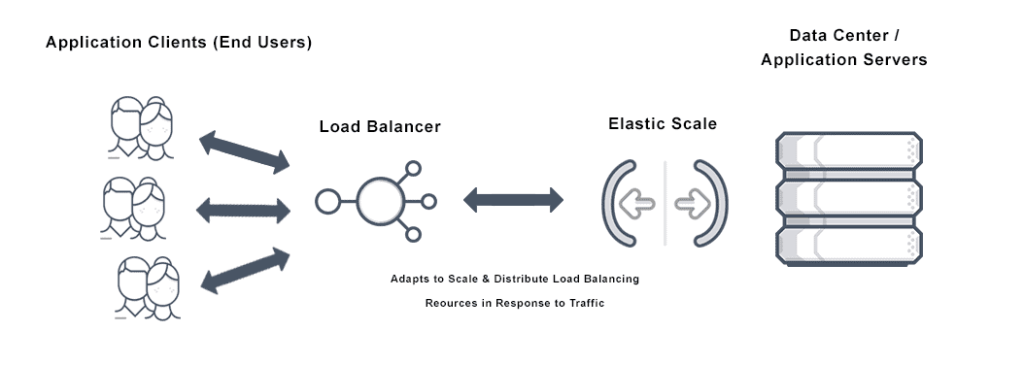
The cloud offers on-demand access to IT resources, allowing businesses to rapidly scale up or down to meet fluctuating workloads like seasonal traffic spikes or new project launches. This elasticity supports faster time-to-market and an agile response to market changes.
Rapid experimentation:
Cloud platforms provide a ready-made environment for developers to build, test, and deploy new applications without hardware limitations or slow procurement processes. This fosters a culture of innovation and accelerates product development.
Access to advanced technologies:
Cloud computing democratizes access to powerful tools like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and big data analytics. This empowers businesses of all sizes to gain data-driven insights and automate complex tasks that were once exclusive to large enterprises.
Enhanced collaboration and business continuity

Seamless remote work and collaboration:
Cloud-based tools like Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, and Zoom enable real-time collaboration among geographically dispersed teams. Employees can access applications and data from any device with an internet connection, which is crucial for modern work models and global service delivery.
Robust disaster recovery (DR):
Cloud providers offer cost-effective and resilient disaster recovery solutions that can be implemented faster than traditional, on-premises setups. Cloud-based backups and failover systems ensure business continuity and minimize data loss in the event of hardware failures, cyberattacks, or natural disasters.
Improved security posture:
Contrary to some perceptions, reputable cloud providers invest heavily in sophisticated security measures like data encryption, access controls, threat monitoring, and automated updates. For many small and medium-sized businesses that lack in-house security expertise, this can result in a more robust security posture than they could achieve on their own.
Key challenges and considerations
Complex cost management:
While cloud computing can be cost-efficient, managing expenses can become challenging without proper governance. Unexpected costs can arise from data transfer fees, unmonitored usage, or improperly sized resources. Implementing a FinOps (Cloud Financial Management) approach is crucial for controlling and optimizing cloud spend.
Downtime and connectivity:
Businesses become reliant on a stable internet connection for accessing cloud services. Outages or poor network performance can disrupt operations, so contingency plans are essential to handle potential service disruptions.
Integration and skill gaps:
Implementing and integrating cloud services with existing legacy systems can be technically complex. Additionally, there may be a need to upskill or hire employees with specific cloud architecture, DevOps, and security expertise to manage solutions effectively.
Future trends of Cloud Computing On Businesses

AI and ML at the core:
AI and machine learning will move beyond being discrete services to become fundamental to cloud operations, enhancing security, resource management, and providing deeper business insights.
Hybrid and multi-cloud strategies:
To gain flexibility and reduce risk, more businesses will adopt hybrid (mixing public and private clouds) and multi-cloud (using multiple providers) approaches as standard practice.
Edge computing:

Driven by the proliferation of IoT devices and the need for real-time data processing, edge computing will process data closer to its source. This reduces latency and bandwidth usage, benefiting applications in areas like smart cities, autonomous vehicles, and real-time analytics.
Quantum computing as a service:
As quantum computing becomes more accessible via cloud platforms, businesses may gain the ability to solve complex problems that are currently beyond the capabilities of classical computers, opening up new avenues for innovation in fields like cryptography and materials science.
Cloud sustainability:
With increased focus on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) commitments, businesses will prioritize cloud providers who are committed to energy efficiency and reducing their carbon footprint.
