The Future of Self-Driving Car
The future of self-driving cars points toward a gradual but transformative shift in transportation, moving from assisted driving to fully automated systems that prioritize safety, efficiency, and new mobility models. While full, Level 5 autonomy in all conditions is still some years away, near-term developments will focus on commercial robotaxis, autonomous freight, and hybrid driving models.
Shift toward shared and commercial mobility

Robotaxis and shuttles:
The first widespread interactions with highly automated vehicles are likely to be through shared services like Waymo and Cruise, which are already operating Level 4 robotaxis in specific, geofenced areas in cities like San Francisco, Phoenix, and Shanghai.
Autonomous freight and logistics:
Self-driving trucks are expected to play a major role in the logistics industry, particularly for long-haul routes on highways. By 2030, autonomous trucking is predicted to be commercially viable, offering increased efficiency, lower operational costs, and a way to address driver shortages.
Declining private car ownership:

As shared autonomous mobility becomes more convenient and potentially cheaper than private ownership, the number of personally owned vehicles in urban areas is expected to decline. This could free up vast amounts of space currently used for parking and roads.
Technological evolution and AI advancements
Enhanced AI and machine learning:
AI is the core technology powering self-driving cars, enabling them to perceive their environment, make real-time decisions, and predict the behavior of other road users. Further advancements in deep learning and sensor fusion will be critical for handling complex, real-world scenarios and navigating challenging weather conditions.
Connectivity and V2X communication:
The rollout of 5G technology will enable fast, low-latency “Vehicle-to-Everything” (V2X) communication, allowing self-driving cars to exchange data with other vehicles, infrastructure like smart traffic lights, and even pedestrians. This will improve traffic flow and enhance overall safety.
Hardware and software integration:
Continued innovation in sensor technology (LiDAR, radar, cameras) and powerful in-vehicle computing platforms will enable vehicles to process immense amounts of data locally (edge computing) for faster and more reliable decision-making.
New business models and urban design
Subscription-based services
Automakers are shifting their business models from traditional car sales toward offering autonomous driving features through subscription plans, providing new revenue streams and allowing consumers to access advanced technology on a flexible basis.
Reimagined vehicle interiors
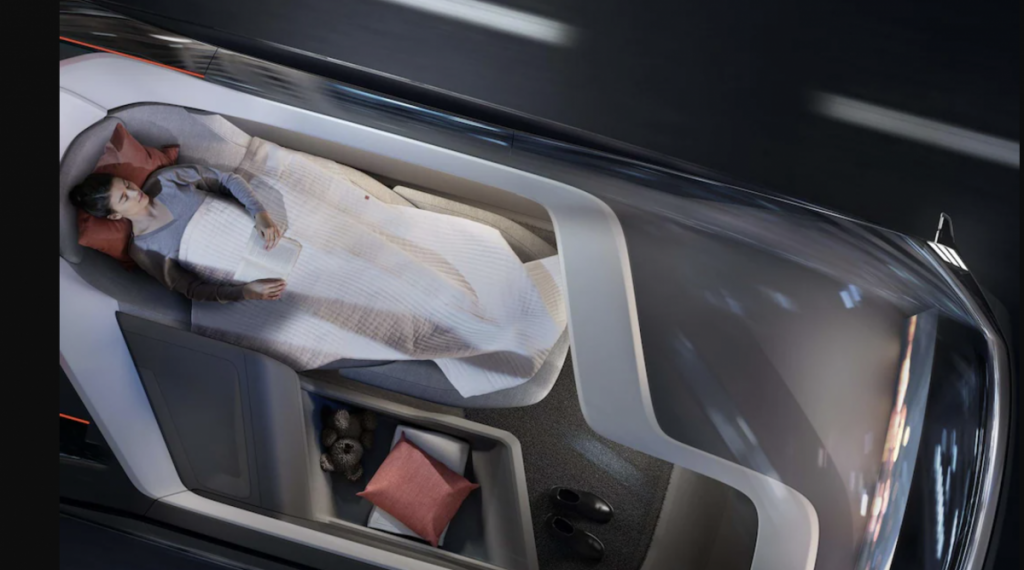

As the focus shifts from driving to riding, car interiors will be redesigned for productivity, relaxation, and entertainment, with features like retractable steering wheels and rotatable seats creating more lounge-like spaces
Smart city integration
: Urban planners are beginning to consider how autonomous vehicles will reshape cities by reducing traffic congestion, optimizing public transit, and repurposing parking lots into pedestrian walkways, parks, or commercial zone
Challenges and considerations
Technological and safety hurdles:
Achieving Level 4 and 5 autonomy still faces significant technical challenges, including handling “edge cases” (rare, complex situations), ensuring reliability in all weather conditions, and developing robust cybersecurity protocols to prevent hacking.
Regulatory and legal frameworks
: Governments worldwide are still grappling with creating consistent laws for self-driving cars, especially concerning liability in case of an accident and standardizing testing and deployment across states and countries
Ethical dilemmas:
Difficult ethical questions remain, such as how an autonomous vehicle should be programmed to make split-second decisions in an unavoidable accident scenario.
Public perception and trust:
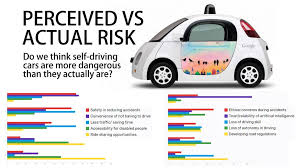
Overcoming public skepticism about entrusting human lives to a machine is a major challenge, especially after high-profile incidents involving autonomous vehicles. Proactive communication and transparent safety data are needed to build confidence.
- Socio-economic impact:
- The widespread adoption of self-driving technology will likely lead to job displacement for professional drivers in the trucking, taxi, and ride-hailing industries, requiring new strategies for retraining the workforce.
Advantages of Self-Driving Car

Self-driving cars offer numerous advantages, primarily centered on enhanced safety, reduced traffic congestion, and increased mobility and convenience for passengers. The core benefits stem from eliminating human error and optimizing driving patterns through advanced technology.
Enhanced safety
Reduced human error:
Government data attributes over 90% of all traffic accidents to human error, including distracted, fatigued, or impaired driving. Self-driving cars aim to eliminate these factors entirely.
Faster and better reactions:
Automated systems can react to hazards faster than humans, see more of their surroundings through 360-degree sensor arrays (LiDAR, radar, cameras), and monitor blind spots with greater vigilance.
Adherence to traffic laws:
Self-driving cars are programmed to obey all traffic laws, such as speed limits and parking regulations, which can reduce speeding tickets and curb-related damage.
Traffic efficiency and environmental gains
Reduced congestion:
Fewer accidents lead to fewer traffic backups. Additionally, self-driving cars can communicate with each other (V2V) and with smart infrastructure (V2X) to optimize traffic flow, reduce stop-and-go waves, and smooth out “phantom traffic jams”.
Fuel efficiency and lower emissions:

Automated “eco-driving” techniques, which involve smoother acceleration, less braking, and optimized routing, lead to lower fuel consumption and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
Optimized urban space:
With a potential shift toward shared robotaxis and improved self-parking capabilities, less space will be needed for parking lots and garages. This could allow for urban areas to be repurposed for parks, housing, or pedestrian zones.
Increased productivity and mobility

Productive travel time:
Passengers can use their commute time to work, read, relax, or catch up on sleep, transforming travel from a chore into an opportunity for other activities.
Economic benefits for businesses:
In the commercial sector, autonomous vehicles can be used for 24/7 delivery services and optimized freight logistics, leading to lower operational costs, increased efficiency, and a solution to driver shortages.
Improved convenience and quality of life
Enhanced ride experience: Car interiors could be redesigned for comfort and entertainment, turning vehicles into mobile leisure or office spaces as the focus shifts away from driving.
Less driving stress and road rage: The elimination of human drivers means fewer aggressive behaviors on the road and a less stressful experience for everyone, which can contribute to better public health outcomes.

Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
YES ! Ask