The Future of Artificial Intelligence in Everyday Life
Introduction to AI’s Evolving Role

Artificial intelligence is no longer a distant concept but a transformative force reshaping how we live, work, and interact. By 2025 and beyond, AI is expected to become even more seamlessly integrated into daily routines, acting as a constant companion that anticipates needs, automates tasks, and enhances experiences across various domains. Predictions suggest AI will evolve from narrow tools like chatbots and search engines to more proactive, agentic systems that handle complex, personalized functions. This shift is driven by advancements in model efficiency, dropping inference costs, and the rise of smaller, decentralized models that run locally on devices.
AI in Home and Personal Life
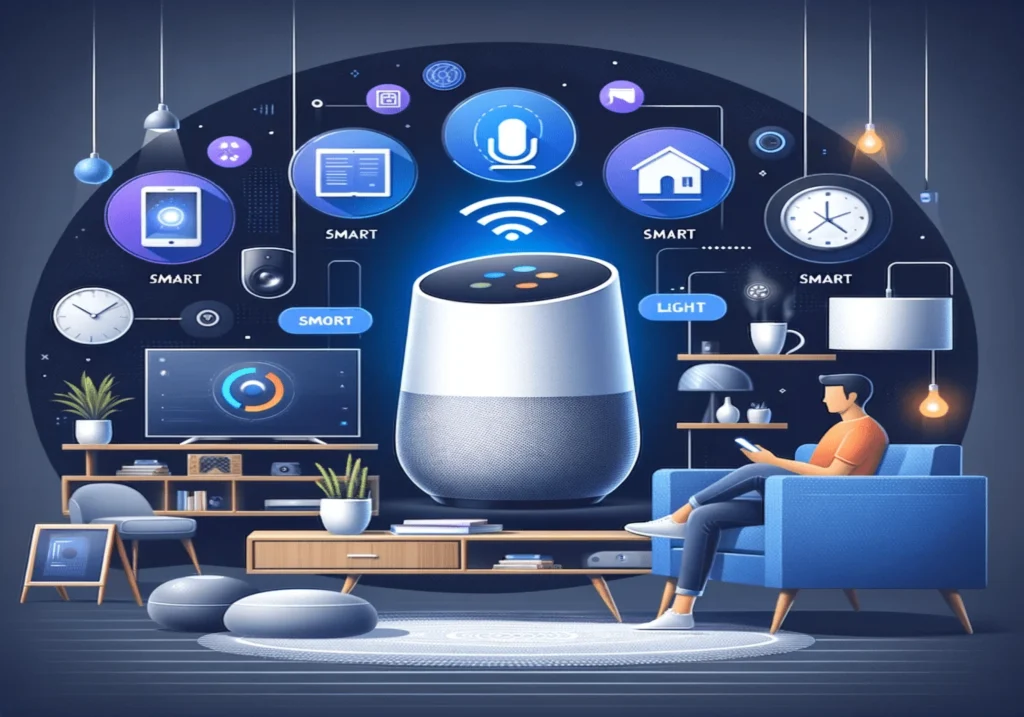
In everyday settings, AI is poised to make homes smarter and more intuitive. By 2025, AI-powered smart homes will automate security, energy management, and daily chores, with devices like fridges acting as nutritionists or alarm clocks as sleep therapists. Personal assistants will go beyond reminders, handling scheduling, email responses, and even social interactions via interoperable agents. Future devices may ditch traditional apps entirely, using local AI to generate customized interfaces on the fly—imagine a task manager or photo editor tailored instantly to your needs.
Robots and wearables will play larger roles, from household companions to augmented reality glasses or smart EVs that enhance mobility and connectivity. AI could even enable brain-computer interfaces for seamless control, turning sci-fi ideas like virtual sidekicks for learning languages or hobbies into reality.

AI in Work and Productivity
At work, AI will amplify human capabilities, automating routine tasks to free up time for creativity. Productivity apps will be rebuilt from the ground up, with AI handling data analysis, decision-making, and even collaborative brainstorming. In consumer apps, models with personalization, context memory, and recommendations will dominate, making tools indispensable once integrated.
Business adoption is surging, with AI fueling efficiency and innovation across industries. However, high human IQ will remain valuable for prompting and guiding AI, as it amplifies rather than replaces creative thinking. Jobs may evolve, with humans focusing on unimagined roles while AI handles the mundane.
AI in Healthcare, Education, and Society
Healthcare will see revolutionary changes, with AI enabling personalized diagnostics, predictive medicine, and life-saving tech like real-time monitoring. In education, smarter systems will offer tailored learning experiences, adapting to individual paces and styles.

Broader societal impacts include enhanced cybersecurity, economic growth, and even decentralized science, where AI accelerates discoveries by individual researchers. Crypto may complement AI by providing verifiable scarcity in areas like identity and money that AI can’t fake.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations

While benefits abound, risks loom: privacy concerns with data sovereignty, ethical dilemmas in model development, and the need for balanced regulation. Public views show growing acceptance but caution, with experts noting AI’s potential to disrupt jobs or amplify biases. Decentralized, ubiquitous AI may mitigate centralization fears, fostering a “garden of smart things” rather than a monolithic system.
In summary, by 2034, AI could be a fixture in nearly every aspect of life, boosting efficiency and innovation while emphasizing human-AI collaboration. The key will be navigating its integration thoughtfully to maximize benefits for all.
There isn’t a single, official logo for “the future of artificial intelligence in everyday life” because AI is a broad concept, but common themes in logos for this idea include abstract technological imagery, such as neural networks or connected data points, often rendered with clean, modern lines and a palette of blue, white, and silver to evoke innovation and intelligence. Logos may also incorporate human-centric elements like an eye or a stylized brain to emphasize the integration of AI with daily human experiences.
Here are some common visual elements you might find in such a logo:
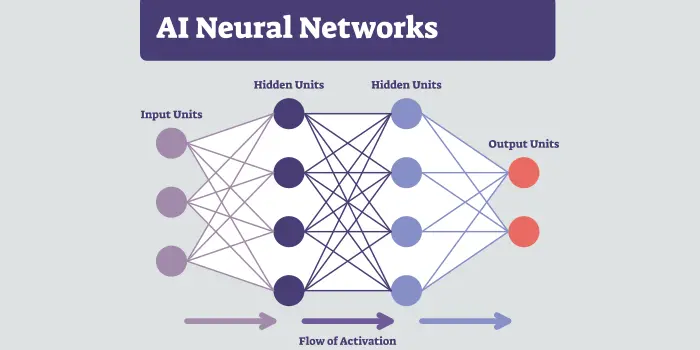
Neural Network & Data Flow:
- Logos frequently feature interconnected nodes, lines, or glowing circuits to represent how AI learns and processes information.
- Layers: Neural networks typically have three types of layers:
- Weights and biases: These are adjustable parameters that determine the strength of connections between nodes and help fine-tune the network’s output.
Abstract Shapes:
- Geometric forms, curves, and digital patterns are used to symbolize advanced technology and the seamless integration of AI into systems.
Abstract shapes are stylized, simplified representations of real-life objects, or they can be non-representational forms created purely for artistic or symbolic purposes. Unlike geometric (e.g., squares, circles) or organic (e.g., leaves, clouds) shapes, abstract shapes often hold meaning through symbolism or cultural understanding rather than literal depiction.
- Logo and graphic design: Abstract shapes are a cornerstone of branding. A well-known logo like the Nike “Swoosh” is an abstract shape that represents movement, speed, and victory.
- Signage and icons: Street signs, app icons, and restroom symbols all use abstract shapes for fast, efficient communication. The simplified image of a bicycle on a traffic sign is an abstract shape that drivers can recognize at a glance.
- Fine art: Movements like Cubism and Geometric Abstraction utilize abstract shapes to move beyond realism.
- Symbolic meaning: Abstract shapes are frequently used as symbols or icons to represent complex ideas, concepts, or emotions in a simple, memorable way.
- Stylized representation: They are created by reducing a real object to its most basic, recognizable elements while removing unnecessary detail. A classic example is a stick figure, which is an abstract shape of a person.
- Cultural context: The meaning of an abstract shape can sometimes depend on shared cultural knowledge. For instance, the gender symbols on a restroom door are abstract shapes that are widely understood in many cultures.
- Focus on form and composition: In fine art, abstract shapes can exist independently of any real-world object. Artists arrange these shapes to explore principles of composition, color, and visual balance, evoking emotional responses purely through form.
Human-AI Interaction
Human-AI interaction (HAII) is the interdisciplinary field dedicated to designing and studying how people and artificial intelligence systems communicate and work together. The goal is to create AI that is user-friendly, trustworthy, and ethically beneficial, often by augmenting human abilities rather than replacing them entirely.

- :Some logos use symbols like an eye, a stylized human silhouette, or hands interacting with digital elements to show how AI will work alongside people.
- Transparency and explainability: AI systems should be able to explain how and why they arrive at a certain decision, especially in critical areas like healthcare or finance. This builds user trust and makes it easier to spot biases or errors.
- User control and feedback: Humans should maintain a sense of control over AI systems and be able to easily correct errors, approve actions, or opt out. AI design should also incorporate feedback loops to learn from user actions and improve over time.
Education and training: AI tutors and adaptive learning platforms can personalize content, respond to a student’s pace, and provide real-time feedback. This augments the teacher’s role by providing valuable insights into student performance.
- Navigating the changing workforce: As AI automates more tasks, there is a risk of job displacement. The future requires investing in reskilling and upskilling programs to prepare workers for new roles that involve human-AI collaboration.
- Designing for a symbiotic future: The future of HAII is likely to be symbiotic, with humans and AI forming deeply integrated, mutually beneficial partnerships. Achieving this will require addressing the ethical, social, and technical challenges of building human-centric AI.
Color Palette
A color palette is a carefully chosen set of colors used in a design or artwork to create a specific mood, brand identity, and visual harmony. The effectiveness of a palette depends on color theory, psychology, and the way colors are combined.
- :Blue, white, silver, and sometimes hints of green are common choices, conveying a sense of intelligence, cleanliness, innovation, and trustworthiness.
Light & Energy
The phrase “Light & Energy by AI” refers to the growing field of applying AI to light-based technologies, particularly to improve energy efficiency, enhance computer vision, and develop a new class of powerful, light-based computers. AI is fundamentally changing how we generate, use, and process light and energy.
Next-generation computing and AI hardware
The relationship between AI and light is now extending to the hardware level, with research focused on creating new, more powerful AI systems that compute with light.
- Photonic neural networks (PNNs): These systems use photons instead of electrons to process information, offering the potential for faster processing speeds and significantly lower energy consumption than traditional electronic neural networks.
- Quantum computing with photons: Some quantum computers use photons to represent qubits. Photonic quantum computing shows promise for handling certain computational tasks at higher speeds and can potentially operate without the extreme cooling required by other quantum systems.
- Smart lighting systems: AI-integrated lighting uses sensors and machine learning to adjust brightness and color based on factors like occupancy, natural light levels, and user preferences. This can reduce lighting energy use by up to 50%.
- Solar energy optimization: AI analyzes weather patterns, historical data, and grid demand to manage solar power systems more effectively. It predicts solar energy generation, optimizes energy storage in batteries, and helps balance supply and demand to increase efficiency and lower costs.
- :The use of glowing elements or light trails can suggest progress, dynamism, and the transformative power of AI.
To find specific examples of logos, you can perform a search on a platform like an AI-powered image generator or a design inspiration website using keywords like: “Future of AI logo, “Artificial intelligence abstract logo, and “Human-AI collaboration logo.


Pingback: Future of smartphones what to expect in 2030 and Beyond - Fact Hub
Pingback: The Role Of Big Data In Decision Making - Fact Hub
Pingback: The Role of Robotics in Modern Industries - Fact Hub
Pingback: ARTIFICAL INTELLIGENCE: The Ultimate Guide to AI for 2025: What You Need to Know: ARTIFICAL INTELLIGENCE: - Fact Hub
Pingback: ELON MUSK`s Bold Ideas That Changed the world. - Fact Hub