The Achievements Of Nikola Tesla

Nikola Tesla (1856–1943), the visionary Serbian-American inventor and electrical engineer, is celebrated as one of history’s most brilliant minds, whose groundbreaking work laid the foundation for the modern electrical age. Born in Smiljan, in what is now Croatia, Tesla’s contributions to electricity, particularly alternating current (AC) systems, revolutionized power distribution. His ambitious pursuits in wireless power transmission foreshadowed contemporary technologies like wireless charging and global communication networks. Despite facing financial hardships and obscurity in his later years, Tesla’s innovations continue to influence everyday life, from household appliances to renewable energy grids and wireless internet. This essay, approximately 1,600 words, explores Tesla’s pivotal achievements in electricity, his pioneering efforts in wireless power, and his enduring impact on modern technology, drawing on his visionary experiments and intellectual legacy.
Tesla’s journey into electrical engineering began in the 1880s, amid the “War of the Currents” between his alternating current (AC) system and Thomas Edison’s direct current (DC) approach. Arriving in the United States in 1884 with little more than a letter of recommendation and a head full of ideas, Tesla quickly joined Edison’s company but soon parted ways due to philosophical differences over AC versus DC.<grok:render card_id=”6ae7c1″ card_type=”citation_card” type=”render_inline_citation”> 3</grok:render> Undeterred, Tesla refined his AC concepts, which allowed for efficient long-distance transmission of electricity—a critical flaw in Edison’s DC system, limited to short distances due to voltage drops.
Tesla’s AC system triumphed at the 1893 World’s Columbian Exposition in Chicago, where it illuminated over 100,000 lights, showcasing its superiority.<grok:render card_id=”1bbd56″ card_type=”citation_card” type=”render_inline_citation”> 3</grok:render> This event, coupled with the successful harnessing of Niagara Falls for AC power in 1895—engineered by Tesla and George Westinghouse—marked a turning point. The Niagara project generated 11,000 horsepower, proving AC’s scalability and reliability for large-scale power distribution.<grok:render card_id=”25925f” card_type=”citation_card” type=”render_inline_citation”> 3</grok:render> These achievements not only ended the War of the Currents but established AC as the global standard, powering homes, industries, and transportation systems today. Tesla’s work in electricity thus democratized energy, making it accessible and affordable on an unprecedented scale.
Understanding Resonance in Tesla Coils
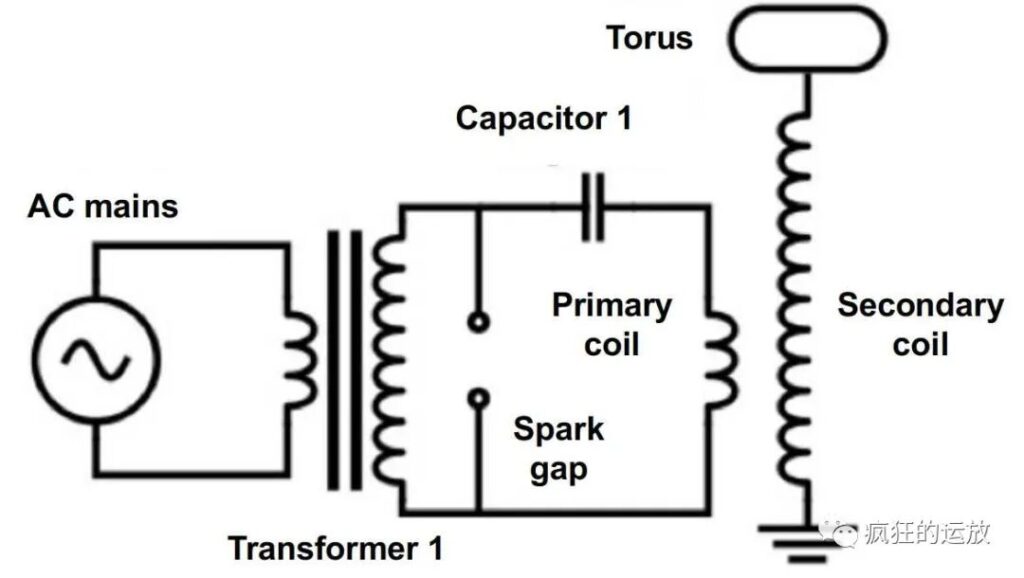
Through public demonstrations in the 1890s, Tesla showcased wireless lighting, where gas-filled tubes glowed without connections, hinting at his broader vision of cordless illumination.<grok:render card_id=”1efb7b” card_type=”citation_card” type=”render_inline_citation”> 4</grok:render> These experiments at his New York laboratory, filled with buzzing coils and crackling discharges, captivated audiences and foreshadowed fluorescent lighting and neon signs. Moreover, Tesla’s high-frequency currents contributed to the discovery of X-rays; he produced shadowgraphs of human hands in 1894, predating Wilhelm Röntgen’s official announcement by a year.<grok:render card_id=”e75e74″ card_type=”citation_card” type=”render_inline_citation”> 3</grok:render> His cautionary notes on radiation’s dangers highlighted his foresight, influencing modern radiology safety protocols.
Visionary Pursuits in Wireless Power
By 1901, funded by J.P. Morgan, Tesla constructed the Wardenclyffe Tower on Long Island, New York—a 187-foot structure intended as a “World Wireless System” for transmitting messages, images, and power worldwide.<grok:render card_id=”02e2b1″ card_type=”citation_card” type=”render_inline_citation”> 0</grok:render> The tower employed a massive Tesla coil to generate low-frequency waves, aiming to ionize the atmosphere and use the ground as a return path for energy.<grok:render card_id=”05a455″ card_type=”citation_card” type=”render_inline_citation”> 4</grok:render> Though financial woes halted completion in 1905, Tesla’s tests successfully lit bulbs 25 miles away, validating the concept.<grok:render card_id=”23d2c4″ card_type=”citation_card” type=”render_inline_citation”> 7</grok:render>
Tesla’s wireless power ideas extended to communication; he envisioned a precursor to the internet, with global broadcasting of news and data.<grok:render card_id=”3749ed” card_type=”citation_card” type=”render_inline_citation”> 2</grok:render> His 1898 demonstration of a radio-controlled boat in Madison Square Garden—the world’s first remote-controlled device—foreshadowed drones and robotics.<grok:render card_id=”d3db33″ card_type=”citation_card” type=”render_inline_citation”> 1</grok:render> Patented as “Method of and Apparatus for Controlling Mechanism of Moving Vessels or Vehicles,” this invention laid groundwork for modern wireless control systems in toys, cars, and missiles.
Despite Wardenclyffe’s demolition in 1917 to settle debts, Tesla’s patents on wireless transmission influenced Guglielmo Marconi’s radio work, for which Marconi won the 1909 Nobel—though the U.S. Supreme Court upheld Tesla’s radio patents in 1943.<grok:render card_id=”ca9e62″ card_type=”citation_card” type=”render_inline_citation”> 3</grok:render> Today, efforts to revive his vision continue; organizations like the Tesla Science Center at Wardenclyffe preserve his legacy, while researchers explore resonant inductive coupling for efficient wireless power.<grok:render card_id=”e4f4d9″ card_type=”citation_card” type=”render_inline_citation”> 0</grok:render>
Influence on Modern Technology

Tesla’s achievements ripple through contemporary innovation, powering the digital and sustainable world. His AC polyphase system underpins global electrical grids, enabling renewable integration like solar and wind farms—ironically, Tesla’s disdain for fossil fuels aligns with today’s green energy push.<grok:render card_id=”8d280c” card_type=”citation_card” type=”render_inline_citation”> 3</grok:render> The induction motor drives electric vehicles (EVs), from Tesla Inc.’s (named in his honor) Model S to industrial automation, comprising 40-50% of global electricity use.<grok:render card_id=”b12e4d” card_type=”citation_card” type=”render_inline_citation”> 3</grok:render>
In wireless power, Tesla’s inductive principles fuel Qi-standard chargers for smartphones and electric toothbrushes, with advancements toward dynamic EV charging on roads.<grok:render card_id=”8b4bae” card_type=”citation_card” type=”render_inline_citation”> 8</grok:render> His work on high-frequency currents informs wireless communication, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and 5G networks, which rely on modulated electromagnetic waves.<grok:render card_id=”6423b0″ card_type=”citation_card” type=”render_inline_citation”> 5</grok:render> The Tesla coil inspires plasma research for fusion energy and medical devices like radiofrequency ablation for tumors.
Tesla’s remote control technology evolved into modern IoT (Internet of Things) devices, smart homes, and autonomous systems. His bladeless turbine, patented in 1913, influences efficient pumps in renewable energy, while his oscillator experiments contributed to seismology and earthquake prediction tools.<grok:render card_id=”1f54a2″ card_type=”citation_card” type=”render_inline_citation”> 3</grok:render> Even in entertainment, Tesla coils feature in music synthesizers and laser shows, echoing his dramatic demonstrations.
The Death of Nikola Tesla

Nikola Tesla, the visionary inventor who revolutionized electricity and pioneered wireless technology, died on January 7, 1943, in New York City. His passing at age 86 marked the end of a life defined by extraordinary contributions to science, overshadowed by personal struggles and financial ruin. Tesla’s death, occurring in relative obscurity at the Hotel New Yorker, was not merely an endpoint but a reflection of his complex legacy—genius unrecognized in his final years yet profoundly influential today. This essay, approximately 1,500 words, examines the circumstances surrounding Tesla’s death, including his declining health, isolation, and the immediate aftermath, as well as the broader significance of his passing in the context of his achievements and enduring impact.

Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me. https://www.binance.info/register?ref=IXBIAFVY
Sure!Ask
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://www.binance.info/register?ref=IXBIAFVY
Thnks