Future of smartphones what to expect in 2030 and Beyond

1.Foldable and roll able designs
Foldable and rollable designs refer to flexible display technologies that allow screens to bend or extend, offering portable and adaptable devices like smartphones, tablets, and TVs. Foldable designs collapse like a book or clamshell, providing a larger screen when unfolded and compact portability when closed, while rollable designs feature a display that can be expanded or retracted from a housing, like a scroll, to change its size on demand. Foldable Designs

These devices use flexible screens that can be bent or creased without damage.
- Examples:
The Samsung Galaxy Z Fold (book-like) and Z Flip (clamshell) are prominent examples of foldable smartphones.
- Benefits:
- Portability: They can be made smaller to fit in pockets or bags.
- Versatility: They offer a large screen for entertainment or work when needed.
- Examples in action:
- A foldable phone might function as a standard smartphone when folded and transform into a tablet-sized screen when unfolded.
- They can also have unique hinged designs, such as the Microsoft Surface Duo with two screens that fold out. Rollable Designs
- How they work:
Unlike foldable screens, rollable displays are designed to retract into a central housing, effectively “rolling” in and out of place to change their size.
- Examples:
While less common than foldables, brands like Samsung have been developing transparent rollable smartphone concepts and other rollable displays for smart TVs.
- Benefits:
- Customizable screen size: Users can expand or shrink the display to suit their needs.
- Potentially larger devices: Rollable technology could allow for very large screens that can be “rolled up” to a manageable size.
- Examples in action:
- A rollable phone could be a standard-sized device that expands to a larger tablet size when needed.
- A rollable TV could have a large screen that retracts into a compact unit when not in use, making it more discreet and versatile.
2.Foldable and roll able designs
Holographic displays create three-dimensional images by diffracting light, offering a realistic, glasses-free way to view 3D content. Unlike traditional 2D displays, they can represent depth by manipulating light direction and intensity, enabling viewers to perceive images in full 3D without needing special eyewear.

How they work
- Light Diffraction:
Holographic displays use holograms, which are essentially interference patterns of light, to reconstruct 3D images.
- Pixel Control:
Instead of simply controlling color and intensity like a regular display, holographic displays control the direction of light from individual points, creating hogels.
- True 3D:
By directing light from many hogels, holographic displays create the illusion of a 3D image that can be viewed from different angles without causing the discomfort of vergence-accommodation conflict (associated with VR headsets). Key Characteristics:
- Glasses-free 3D:
They allow viewers to see 3D images without needing special glasses or headsets.
- Realistic Depth:
They aim to replicate the depth perception of the real world, including effects like parallax, blur, and occlusion.
- Potential for Immersive Experiences:
Holographic displays are considered a promising technology for creating immersive virtual experiences. Limitations:
- Form Factor:
Holographic displays can have limitations in terms of their physical size and shape.
- Image Quality:
Factors like light modulation, imperfections in the optical system, and mismatches between simulation and reality can affect image quality.
- Cost:
Holographic display technology is still evolving and can be expensive, especially for high-end systems. Examples:
- Looking Glass Factory: Offers holographic displays for personal and professional use.
- Hyundai Mobis and Zeiss: Collaborating on holographic windshield displays for vehicles.
- Holoconnects: Specializes in holographic displays for advertising and events.
3.Ai powered personal assistant
An AI-powered personal assistant for smartphones refers to software that uses artificial intelligence (AI) to help users perform tasks, answer questions, manage schedules, control smart devices, and more—via voice or text input. These assistants are deeply integrated into modern smartphones.
Popular AI-Powered Personal Assistants on Smartphones
Assistant Platform Key Features
Apple (iOS, iPadOS, Voice commands, smart home control (HomeKit),
Siri
macOS) Siri Shortcuts, system integration
| Assistant Platform | Key Features |
| Google Assistant Android, iOS | Natural language understanding, real-time translation, Google ecosystem integration |
| Bixby Samsung (Android) | Samsung ecosystem integration (TVs, SmartThings), scene-based automation, deep app control |
| Alexa (via app) Android, iOS | Works with Amazon devices, routines, smart home control |
| Cortana Windows/Android/iOS (discontinued) (was) | Was focused on productivity with Microsoft 365 |
| ChatGPT (via iOS, Android app) | Advanced natural conversation, multimodal (text, voice, image), coding help, content generation |

Capabilities of Modern AI Assistants
- Voice interaction: Use voice to set reminders, send texts, call contacts.
- Context awareness: Understand context (e.g., location, time, recent queries).
- Personalization: Learn from user preferences and behavior.
- Automation: Create routines (e.g., “Good morning” to read weather + calendar + news).
- Smart home integration: Control smart lights, locks, thermostats.
- Multilingual support: Translate or switch languages on the fly.
- Generative AI: Tools like ChatGPT and Gemini can now write emails, summarize articles, or help with creative writing.

Example Use Case
User: “Hey Siri, remind me to call Mom when I get home.” Siri: “Okay, I’ll remind you to call Mom when you arrive home.”
Or using ChatGPT’s mobile app:
User: “Summarize this email and draft a reply thanking them for the update.”

Emerging Trends
- AI copilots: Tools like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Copilot are evolving from assistants into copilots—proactive, multimodal AI that help with writing, planning, learning, and coding.
- Offline functionality: Increasing number of AI tasks can be processed on-device (e.g., Apple’s Private Cloud Compute).
- Custom voice agents: Users can now customize their assistant’s voice, personality, and skills (e.g., OpenAI’s “Custom GPTs”).
4.No more Screen
What’s Replacing Smartphones?
Here are some screenless AI-powered personal assistant devices and platforms designed for this post-smartphone future:
- Humane AI Pin (No Screen)
- Form: Worn on your clothing (like a pin)
- Interaction: Voice + gesture + laser projection (optional)
- Assistant: AI-powered by large models (including GPT-4)
- Connectivity: Has its own cellular plan — no phone needed
- Use cases: Send messages, get directions, ask questions, manage schedule
Pros: 100% screenless, wearable, cutting-edge
Cons: Expensive, still limited features compared to phones
- Rabbit R1 (Minimal Screen, Voice-First)
- Form: Pocket-sized AI gadget
- Interaction: Button + voice (screen is minimal, not essential)
- Assistant: Rabbit OS powered by LAMs (Large Action Models)
- Goal: Replace apps with voice-based task execution
Pros: Executes real-world tasks via voice
Cons: Not truly screenless, still in early development
- Smart Earbuds + AI Assistant
- Examples:
o Pixel Buds Pro + Google Assistant o AirPods Pro + Siri o Echo Buds + Alexa
- Interaction: Wake word + voice
- Phone needed? Yes, but it can stay in your pocket or at home with some models using cloud connections via Wi-Fi or LTE earbuds.
Pros: Mature tech, good voice recognition, real-world use
Cons: Still tied to a phone in most cases
- Standalone Voice Assistants (Ambient AI)
- Amazon Echo Frames (glasses)
- AI necklaces (startups developing)
- AI ear-wear (startups exploring this too)
These aim for ambient, always-on AI, wearable, voice-controlled, and fully screenless.
- Future Options (2025–2026)
- Apple and Google are rumored to be working on AI-first wearables (e.g., smart rings, glasses, pins).
- On-device AI chips now enable assistants to work offline, faster, and more privately — no phone required.
How You Can Start Living “Screen-Free” Now
If you’re serious about ditching the phone:
Option 1: Try the Humane AI Pin
- Buy the pin
- Activate LTE plan
- Pair with earbuds for private voice responses
- You’re now living screen-free
Option 2: Use AI Earbuds + Wi-Fi
- Use smart earbuds (Pixel Buds or Echo Buds)
- Leave your phone at home
- Interact only by voice
5.6G &beyond Net Work

6G will launch commercially around 2030, building on 5G to provide faster speeds, lower latency, and integrate communication with sensing and computation capabilities. This will enable a new era of immersive applications like holographic communication, Extended Reality (XR), and integrated AI, where networks are more intelligent, and devices become simpler and less power-intensive.
Key characteristics of 6G:
- Integrated Communication & Sensing:
6G networks will uniquely combine communication, computation, and sensing, allowing devices and the network itself to “feel” their environment.
- Higher Frequencies & Bandwidth:
6G will operate at significantly higher frequencies, possibly in terahertz bands, to support massive data rates and network density.
- AI-Native Networks:
Artificial Intelligence will be a core component, used for network automation, optimization, and enabling new services.
- Ultra-Low Latency:
6G aims for microsecond latency (one-thousandth of a millisecond), enabling psychologically invisible, real-time communication experiences.
- Computational Capabilities:
6G will integrate computing functions within the network, allowing devices to offload computation for complex tasks and reducing their power consumption. Impact on Smartphones and Devices:
- Simpler, Lighter Devices:
With computing functions integrated into the network, user devices can become simpler, smaller, and require less power.
- Enhanced Experiences:
Smartphones and other devices will leverage the network’s sensing and computation capabilities for more advanced applications.
Potential Applications:
- Holographic Communication: Immersive, multi-dimensional interactions and experiences.
- Immersive Extended Reality (XR): Deeper integration of digital and physical realities for work and leisure.
- Smart Health and Traffic Control: Real-time environmental monitoring and control with integrated sensing.
- Ubiquitous AI: AI becoming an intrinsic part of the network for improved efficiency and new intelligent services.
6.Eco friendly & self charging phones

Currently, self-charging phones are not commercially available; however, the solar-powered power station is a practical eco-friendly way to charge your existing phone without traditional electricity, and battery manufacturers are working on new self-charging technologies for future consumer electronics, notes
Eco-Friendly Charging Options
- Solar power stations:
These devices harness solar energy to charge your phone and other electronics, providing an alternative to traditional power sources.
- Eco-friendly accessories:
Look for accessories made from recycled materials, such as the wireless charging pads made from bamboo [Link: search result 5,img2,img3,img4].
25,996,094
16
·
0
The Future of Self-Charging Phones
- New technologies:
Companies like Nichicon and Epishine are developing self-charging battery solutions using technologies like printed organic solar cells.
- Energy harvesting:
Researchers are exploring new energy harvesting materials and techniques to enable future smartphones to charge themselves [Link: search result 5,img7]. How to Improve the “Greenness” of Your Current Phone
- Use power-efficient settings: Adjust your phone’s power-saving modes to reduce battery consumption.
- Opt for older, durable models: Choosing an older but still-functional phone instead of constantly upgrading can reduce electronic waste.
7.Built in augmented reality (AR)

Built-in augmented reality” describes AR capabilities that are integrated directly into a device, rather than requiring separate hardware or addons, allowing users to experience augmented reality by overlaying digital information onto the real world using a device’s camera, sensors, and display. This can be seen in smartphones with AR apps using platforms like Apple’s ARKit or Google’s ARCore, or in dedicated devices like AR glasses.
- Sensing the Environment:
The device’s camera and sensors (like accelerometers and LiDAR) capture the real world.
- 2. Spatial Understanding:
Algorithms and AI process this data to understand the environment’s surfaces, depth, and the device’s position and orientation in 3D space.
- 3. Digital Overlay:
Computer-generated content, such as 3D models, text, or images, is rendered onto the real-world view through the device’s screen.
- 4. Integration:
The digital information is seamlessly integrated with the physical world, creating an enhanced, mixed-reality experience. Examples of built-in AR:
- Mobile AR:
Many smartphone and tablet apps utilize AR for games, filters, and utility features, like virtually placing furniture in a room before purchase.

- Smart Glasses and Headsets:
Devices like the Apple Vision Pro integrate AR to display digital content within the user’s physical environment, such as photos on a wall or directional guides.

Apple’s RealityKit and Google’s ARCore are frameworks that allow developers to create these integrated AR experiences for mobile devices.
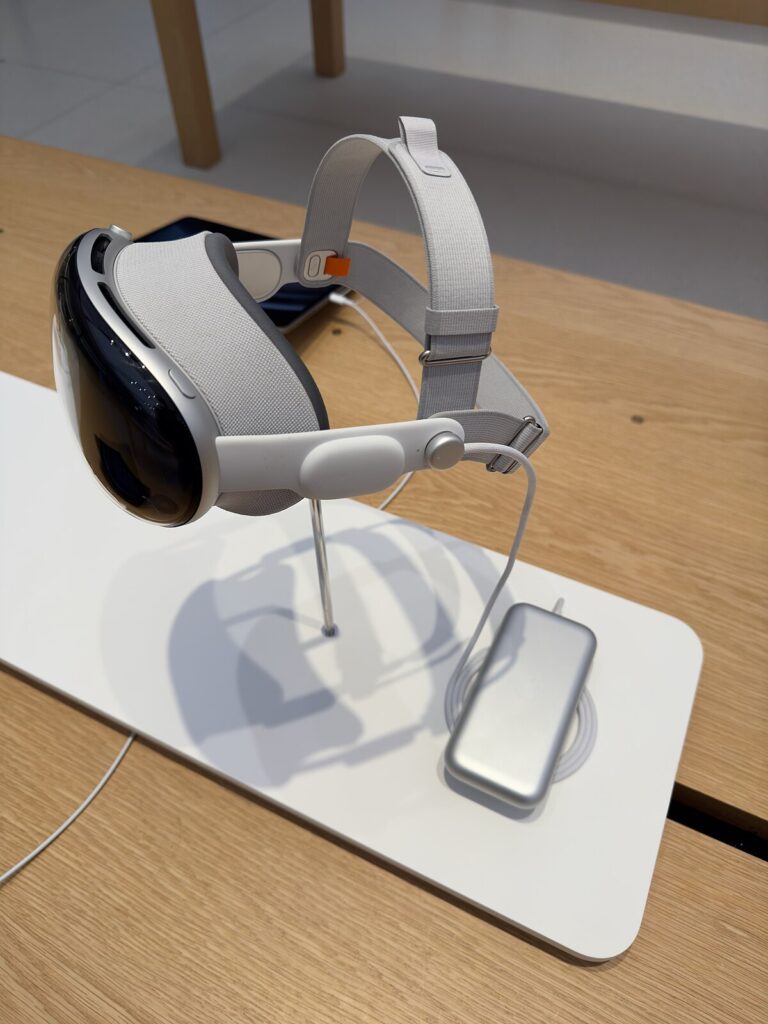

8.Ultra secure biometric system

For ultra-secure biometric systems on smartphones, look for devices with advanced features like 3D facial mapping (e.g., Apple’s Face ID) or ultrasonic fingerprint sensors, coupled with dedicated security chips like Apple’s Secure Enclave or Google’s Titan M2 to isolate sensitive data. High-security phones like the Google Pixel 9 Pro and Samsung Galaxy S25 Ultra incorporate these features alongside robust OS-level security and regular updates to protect against evolving threats. For the highest security, consider privacy-focused operating systems like GrapheneOS for Android devices, which offers advanced sandboxing and control over data sharing.
Advanced Biometric Systems
Face ID (Apple):
Uses 3D facial mapping for high accuracy in unlocking and authenticating within apps, providing a strong line of defense.
Ultrasonic Fingerprint Scanners (Samsung/Google):
These sensors read pressure points under the skin, making them harder to spoof than traditional optical sensors.
Dedicated Hardware Security
Secure Enclave (Apple):
A dedicated security processor that isolates sensitive data, such as biometric templates and encryption keys, from the main operating system.
Titan M2 Security Chip (Google):
A similar dedicated hardware module in Google Pixel phones that handles sensitive operations in a secure, isolated environment to prevent tampering and malware. Integrated Security Platforms
- Samsung Knox: A multi-layered security platform that protects data from the chip to the cloud, including features like secure boot, hardware encryption, and a secure folder for private files.
Operating System Security
- Google Pixel with GrapheneOS:
For extreme security on Android, installing the GrapheneOS operating system on a Google Pixel offers a hardened system, sandboxing for apps, and control over data sharing, including the option to run without Google services.
- Regular OS and Security Updates:
Choosing a phone that receives long-term, regular security patches is crucial to protect against new threats and vulnerabilities.
Recommended Devices
- Google Pixel 9 Pro / Pixel 9 Pro XL:
Offers advanced face unlock for banking, a fast fingerprint sensor, and a dedicated Titan M2 chip, with the option to install privacy-focused GrapheneOS.
- Samsung Galaxy S25 Ultra:
Features Samsung Knox for layered security, along with biometric unlock options, hardware encryption, and a secure folder for sensitive information.
- Apple iPhone (e.g., iPhone 16 Pro Max):
Known for its robust Face ID system and the Secure Enclave, providing high-level security for biometric data and overall system protection.
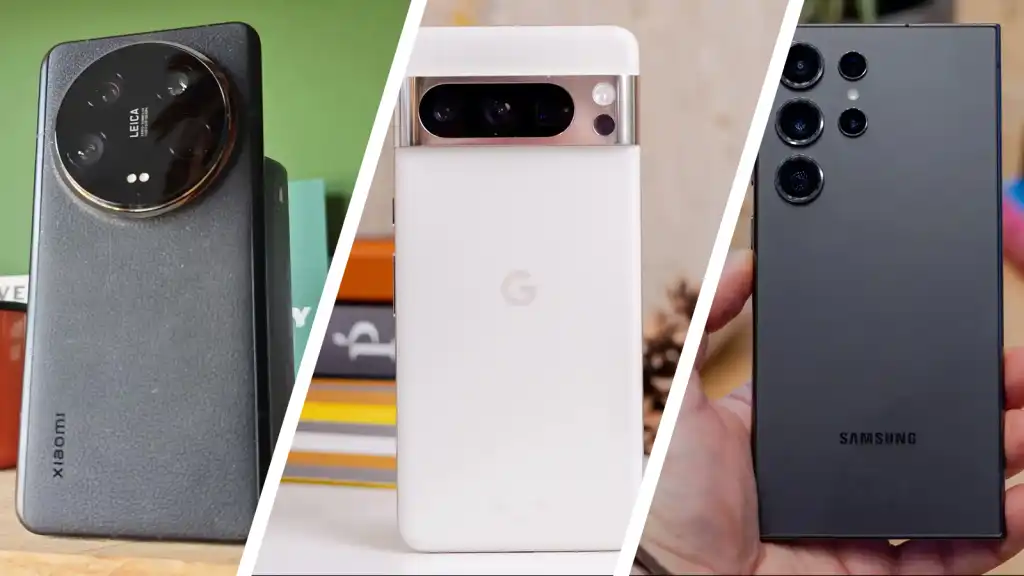
9.Smarter cameras
Smarter cameras” in smartphones leverage Artificial Intelligence (AI) to enhance photos and videos through features like advanced image processing, automatic scene detection, optical and digital zoom, sophisticated portrait modes with professional-grade bokeh effects, and real-time video enhancements. Top camera phones in 2025 include models like the Apple iPhone 16 Pro Max for overall video capabilities, the Google Pixel 9 Pro series for its comprehensive AI features and excellent night photography, and
the Samsung Galaxy S25 Ultra for its advanced AI camera system and versatility. Other excellent options for photo and video quality are the Xiaomi 15 Ultra and the Vivo X200 Pro.
Key features of smarter smartphone cameras
- AI-powered image processing:
AI algorithms improve image quality, color accuracy, and detail, especially in challenging lighting conditions.
- Advanced zoom:
Optical and advanced AI-driven digital zoom provide high-quality, clear images even at significant distances.
Portrait Mode and Bokeh:
AI creates professional-looking background blur (bokeh) for portraits, often on par with professional cameras.
- Video enhancements:
Smart cameras offer features like 4K Dolby Vision recording, professional log video options, and advanced stabilization.
- Smart editing tools:
Features like AI-enhanced editing tools allow users to transform photos and videos after they’ve been captured.
Top camera phones for 2025
Apple iPhone 16 Pro Max:
Known for its exceptional video quality and advanced clarity, making it ideal for vloggers.
- Google Pixel 9 Pro Series:
Excels in capturing sharp, colorful images day or night, with powerful AI capabilities and advanced zoom.
- Samsung Galaxy S25 Ultra:
Features an advanced AI camera system and a powerful, versatile performance for daily use and photography.
- Xiaomi 15 Ultra:
Boasts an exceptionally high-quality telephoto zoom camera that can serve as the primary camera and offers professional-grade 8K video.
Vivo X200 Ultra:
Features a unique combination of advanced lenses and sensors, providing impressive detail, color, and background blur for both photos and videos.

10.End of physical sims ports
The end of physical SIM card ports on smartphones is becoming a reality, driven by the increasing adoption of eSIM technology, which offers advantages like space savings for manufacturers, instant and digital activation for users, and improved security. While many Android phones still retain a physical slot alongside eSIM support, Apple has already transitioned to eSIMonly models in certain regions, like the United States, with its iPhone 14 series, signaling a future trend for the entire industry.
An eSIM is a digital, embedded Subscriber Identity Module that eliminates the need for a physical SIM card, allowing for over-the-air activation and storage of multiple mobile network profiles on a single device. eSIMs provide convenience and flexibility by enabling digital plan activation, easy switching between carriers, and support for multiple numbers, which is particularly useful for international travel. To activate an eSIM, you typically scan a QR code provided by your mobile carrier, connect your device to the internet, and navigate to the device’s cellular settings to add a new cellular plan.
What is an eSIM?
- Digital SIM:It’s a virtual or digital SIM card embedded directly into your phone’s hardware.
- No Physical Card:Unlike traditional SIM cards, you don’t need to insert or remove a physical card to activate a mobile number or switch carriers.
- Remote Activation:An eSIM allows you to activate a mobile number and change your service provider digitally, without visiting a store.
Key Features and Benefits
- Flexibility:You can digitally activate and store multiple network profiles and numbers on a single device, making it easy to switch between carriers or plans.
- Convenience:It simplifies the activation process and eliminates the hassle of managing physical SIM cards.
- Travel-Friendly:eSIMs are excellent for international travel, as you can easily download data plans for different countries without needing to buy a physical SIM upon arrival.
- Security:With a built-in digital SIM, there’s no physical card to lose or steal.
How to Activate an eSIM
- 1. Obtain a QR Code:Visit your mobile carrier’s website or customer service center to get a QR code for your eSIM.
- 2. Connect to the Internet:Ensure your device is connected to a Wi-Fi network.
- 3. Scan the QR Code:On your phone, go to the cellular settings and select the option to add a new cellular plan.
- 4. Launch the Camera:Your phone’s camera will automatically launch, allowing you to scan the provided QR code.
- 5. Download and Activate:After scanning, the eSIM profile will download to your device, and your eSIM will be ready to use.
- Space Savings:
Eliminating the physical SIM slot frees up internal space in smartphones, allowing for larger batteries, more advanced camera modules, or other hardware.
- Digital Activation:
Users can activate a cellular plan by downloading credentials via a QR code or through their operator’s app, eliminating the need to wait for a physical card to arrive.
- Enhanced Security:
eSIMs offer stronger security through remote management and stronger authentication methods, making them more resistant to scams like port-out scams.
- Flexibility:
Users can easily switch between mobile networks and manage multiple plans on a single device, even using one for personal and another for business use or for international roaming.
- Environmental Benefits:
Reducing the production and disposal of physical SIM cards offers a significant sustainability benefit by cutting down on plastic waste. Current Landscape
- Apple’s Move:
Apple has been a key driver of the shift, with its iPhone 14 models in the US being eSIM-only.
- Android’s Approach:
Most Android phones still include physical SIM slots, but they are increasingly supporting eSIM as well.
- Industry Adoption:
While adoption is growing, many carriers worldwide still need to offer comprehensive eSIM support for mass adoption to become standard. The Future
- Portless Phones:
The trend suggests that portless phones will become more common, not just for SIM cards but for charging as well, with technologies like MagSafe on the iPhone paving the way.
- Beyond Smartphones:
eSIM technology is also poised to expand to other devices like tablets, laptops, and wearables, enabling standalone cellular connectivity.
Pingback: The history of evolution of smartphones - Fact Hub
Pingback: The Truth About Artifical Intelligence in Daily Life - Fact Hub